Shuji Nakamura, the recipient of the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics and former ECS Plenary speaker, is awarded for his invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes.
Credit: Randall Lamb
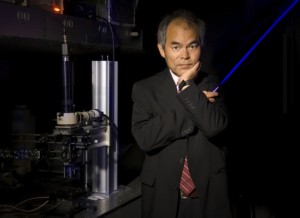
The 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded to Shuji Nakamura, professor of materials and of electrical and computer engineering at the University of California and 2010 ECS Plenary speaker.
The prize is for the invention of efficient blue light-emitting diodes, which has enabled bright and energy-saving white light sources, and is shared with ECS member Isamu Akasaki of Meijo University and Nagoya University, Japan; and Hiroshi Amano of Nagoya University.
In his plenary talk at the 218th ECS Meeting in Las Vegas, Nevada, Nakamura described the current status of III-nitride based light emitting diodes (LEDs) and laser diodes. Nitride-based white LEDs have been used for many application such as LCD TV backlight, lighting for inside/outside applications and others.
According to the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, when Nakamura, Akasaki and Amono “produced bright blue light beams from their semiconductors in the early 1990s, they triggered a fundamental transformation of lighting technology. Red and green diodes had been around for a long time, but without blue light, white lamps could not be created. Despite considerable efforts, both in the scientific community and in industry, the blue LED had remained a challenge for three decades.”
The LED lamp “holds great promise for increasing the quality of life for over 1.5 billion people around the world who lack access to electricity grids,” the academy continued.
Here’s a list of articles in the ECS Digital Library written by the 2014 Physics Nobel Prize Winners. You can look at them for free:
Hiroshi Amano and Isamu Akasaki
Widegap Column-III Nitride Semiconductors for UV/Blue Light Emitting Devices
Growth and Luminescence Properties of Mg-Doped GaN Prepared by MOVPE
Isamu Akasaki
Epitaxial Growth and Properties of AIxGal.xN by MOVPE
Etching Characteristics and Light Figures of the {111} Surfaces of GaAs
Shuji Nakamura
Piezoelectric Field in Semi-Polar InGaN/GaN Quantum Wells
Read more about Shuji Nakamura’s plenary talk.
Read more about 2014 Nobel Prize winners for Physics.