Long-time ECS member, editor of the Journal of The Electrochemical Society, and Distinguished University Professor at Case Western Reserve Robert Savinell has a new title to add to his list. Savinell will lead the U.S. Department of Energy’s new Energy Frontier Research Center at Case Western Reserve University, in support of a research endeavor that focuses on identifying new battery chemistries with the potential to provide large, long-lasting energy storage solutions for buildings or the power grid. The project is made possible by an EFRC grant, which awarded $10.75 million to Case Western Reserve University, allowing the school to establish a research center to explore Breakthrough Electrolytes for Energy Storage.
Long-time ECS member, editor of the Journal of The Electrochemical Society, and Distinguished University Professor at Case Western Reserve Robert Savinell has a new title to add to his list. Savinell will lead the U.S. Department of Energy’s new Energy Frontier Research Center at Case Western Reserve University, in support of a research endeavor that focuses on identifying new battery chemistries with the potential to provide large, long-lasting energy storage solutions for buildings or the power grid. The project is made possible by an EFRC grant, which awarded $10.75 million to Case Western Reserve University, allowing the school to establish a research center to explore Breakthrough Electrolytes for Energy Storage.
Change isn’t easy. For women, it took lobbying, protests, campaigns, and even jail time to receive the right to vote. It wasn’t until August 26, 1920, when women’s fight for change finally paid off. The Nineteenth Amendment was added to the United States Constitution, giving women the right to vote as citizens of the United States, regardless of their sex. Today, we celebrate women, their achievements, and the continued need for change.
 Some people crack under pressure. Not Vilas Pol. The chemical engineering professor from Purdue University was in his element as he raced to assemble the periodic table in record time, 8 minutes and 36 seconds to be exact, setting a new Guinness World title. With all 118 elements set in place, Pol raised his hands, celebrated his new title as the fastest man to arrange all the elements of the modern periodic table. The never before attempted world record was completed on Wednesday, August 15, 2018.
Some people crack under pressure. Not Vilas Pol. The chemical engineering professor from Purdue University was in his element as he raced to assemble the periodic table in record time, 8 minutes and 36 seconds to be exact, setting a new Guinness World title. With all 118 elements set in place, Pol raised his hands, celebrated his new title as the fastest man to arrange all the elements of the modern periodic table. The never before attempted world record was completed on Wednesday, August 15, 2018.
 Lithium-ion batteries play a major role in our everyday lives; they’re in our cell phones, solar panels, tablets, cars, and medical devices, to name a few. All these modern technologies are made possible because of batteries. Yet, they’re far from perfect. The Samsung Note 7 self-combusted on nightstands and planes in 2016, injuring customers and causing second-degree burns in one Florida man. Not to mention, the hoverboard’s explosion around the same time, causing a recall of roughly 16,000 hoverboards.
Lithium-ion batteries play a major role in our everyday lives; they’re in our cell phones, solar panels, tablets, cars, and medical devices, to name a few. All these modern technologies are made possible because of batteries. Yet, they’re far from perfect. The Samsung Note 7 self-combusted on nightstands and planes in 2016, injuring customers and causing second-degree burns in one Florida man. Not to mention, the hoverboard’s explosion around the same time, causing a recall of roughly 16,000 hoverboards.
 In the remote hills of the Appalachian Mountains lies what’s considered the gold of today’s day and age — Quartz, the basis of the modern computer chip. A recently published Wired article, The Ultra-Pure, Super-Secret Sand That Makes Your Phone Possible, discusses the pristine sand, a key player in manufacturing the silicon used to make the chips. From the processor in your laptops to the processor in your cell phones and tablets, all of which likely derived from the sand.
In the remote hills of the Appalachian Mountains lies what’s considered the gold of today’s day and age — Quartz, the basis of the modern computer chip. A recently published Wired article, The Ultra-Pure, Super-Secret Sand That Makes Your Phone Possible, discusses the pristine sand, a key player in manufacturing the silicon used to make the chips. From the processor in your laptops to the processor in your cell phones and tablets, all of which likely derived from the sand.
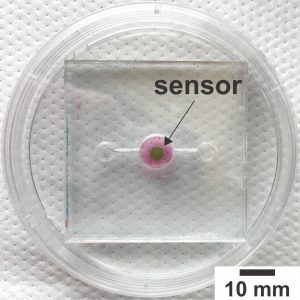
A new biosensor has been developed that allows researchers to track oxygen levels in real time in “organ-on-a-chip” systems, according to North Carolina State University. The organ-on-a-chip makes it possible to ensure that bodily systems more closely mimic the function of real organs. The goal is to use these organs-on-a-chip to expedite drug testing and development by evaluating the effectiveness of new drugs with small-scale, biological structures that mimic a specific organ function, such as transferring oxygen from the air into the bloodstream in the same way that a lung does.
 Electric vehicles don’t only move people, they move companies too. And Volkswagen is making big moves when it comes to investing in battery-powered vehicles.
Electric vehicles don’t only move people, they move companies too. And Volkswagen is making big moves when it comes to investing in battery-powered vehicles.
According to an article in AXIOS written by Eric Wachsman, director of the Maryland Energy Innovation Institute at the University of Maryland, founder of Ion Storage Systems, and 3rd vice president of the ECS board of directors, in June alone, Volkswagen invested $100 million in QuantumScape, a solid state battery startup. And now, the car company is considering building a factory in Europe to produce solid state batteries, a next-generation battery technology, to power their electric vehicles. Volkswagen isn’t alone. Solid-electrolyte batteries are getting international attention from companies like Toyota, Nissan, Dyson, and BMW, who’ve all made similar investments. (more…)
 In 1888, German inventor Andreas Flocken created what is widely considered the world’s first electric car. According to The Battery Issue, recently published by The Verge, the 900-pound vehicle drove at the top speed of nine miles per hour, coming to a halt after a two and a half hour test ride. Although it was considered a success, it wasn’t entirely. The car’s battery, sustainably charged with water power, had died.
In 1888, German inventor Andreas Flocken created what is widely considered the world’s first electric car. According to The Battery Issue, recently published by The Verge, the 900-pound vehicle drove at the top speed of nine miles per hour, coming to a halt after a two and a half hour test ride. Although it was considered a success, it wasn’t entirely. The car’s battery, sustainably charged with water power, had died.
Today, nearly 130 years, German carmakers are still having trouble with their batteries – specifically with battery cells. As a result, car companies are relying on suppliers from China, Korea, and Japan for the highly needed component.
“Cells can be a major technology differentiator and cells are the by far most costly part of the battery pack,” says Martin Winter, a professor of materials science, energy, and electrochemistry at the University of Münster and ECS Battery Division and Europe Section member. Winter says a large scale production of battery cells by European or German companies will be crucial in order to take part in the “enormous and rapidly growing market.”
 Join The Electrochemical Society on August 19–23 at the 256th ACS National Meeting & Exposition in Boston, MA.
Join The Electrochemical Society on August 19–23 at the 256th ACS National Meeting & Exposition in Boston, MA.
The ACS meeting is a great opportunity for ECS to connect with our members and other interested scientists, researchers, and academics to discuss what’s new and exciting in the field and with ECS. The ACS meeting offers a place for chemistry professionals to meet and share ideas. There will be over 16,000 attendees and over 300 exhibitors at this year’s Boston meeting, offering workshops, career training, social events, new technology and research, and career development opportunities.
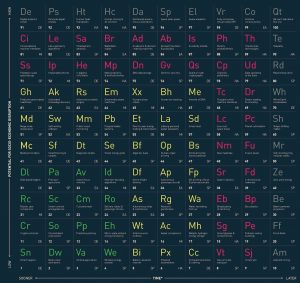
The future may seem intangible, but according to Business Insider, Academics at Imperial Tech Foresight are helping us grasp just what it might look like. Inspired by the periodic table of chemical elements, the academics replaced its contents with elements we may very well one day see.
The predictions are slotted into a space across two axis: The Y-axis ranks the potential for disruption from high to low, while the X-axis determines how soon it will become a reality. All elements are also color-coded to reflect the present, 20 years into the future, and up to the far away future.
For example, green elements are a reality now: Cm – Cultured meat, Pp – Predictive policing, and Rc – Robotic care companions.
And yellow elements are those that may occur in the near future: Em – Emotionally aware machines, Mm – Public mood monitoring, and Bs – Artificial human substitutes.