By: Neal Dawson-Elli, Seong Beom Lee, Manan Pathak, Kishalay Mitra, and Venkat R. Subramanian
This article refers to a recently published open access paper in the Journal of The Electrochemical Society, “Data Science Approaches for Electrochemical Engineers: An Introduction through Surrogate Model Development for Lithium-Ion Batteries.”
Data science is often hailed as the fourth paradigm of science. As the computing power available to researchers increases, data science techniques become more and more relevant to a larger group of scientists. A quick literature search for electrochemistry and data science will reveal a startling lack of analysis done on the data science side. This paper is an attempt to help introduce the topics of data science to electrochemists, as well as to analyze the power of these methods when combined with physics-based models.
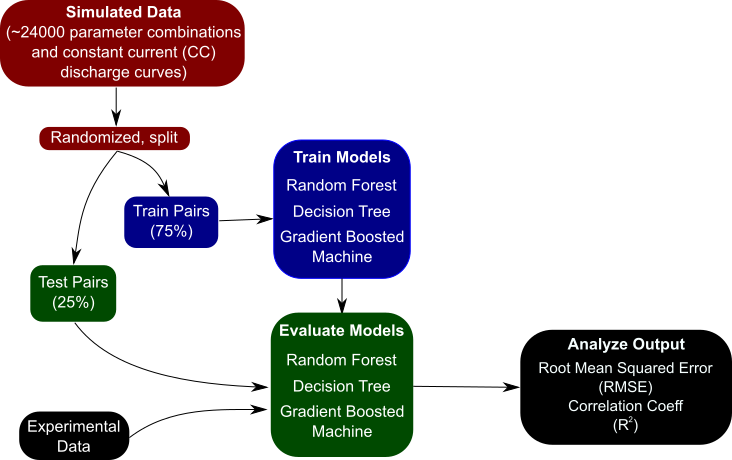
At the core of the paper is the idea that one cannot be successful treating every problem as a black box and applying liberal use of data science – in other words, despite its growing popularity, it is not a panacea. The image shows the basic workflow for using data science techniques – the creation of a dataset, splitting into training-test pairs, training a model, and then evaluating the model on some task. In this case, the training data comes from many simulations of the pseudo two-dimensional lithium-ion battery model. However, in order to get the best results, one cannot simply pair the inputs and outputs and train a machine learning model on it. The inputs, or features, must be engineered to better highlight changes in your output data, and sometimes the problem needs to be totally restructured in order to be successful.

 A team of researchers from the Joint Center for Energy Storage Research is taking a potential major step toward developing energy dense, safe solid state magnesium-ion batteries.
A team of researchers from the Joint Center for Energy Storage Research is taking a potential major step toward developing energy dense, safe solid state magnesium-ion batteries. Capitalizing on tiny defects can improve electrodes for lithium-ion batteries, new research suggests.
Capitalizing on tiny defects can improve electrodes for lithium-ion batteries, new research suggests. A new sodium-based battery can store the same amount of energy as a state-of-the-art lithium ion at a substantially lower cost.
A new sodium-based battery can store the same amount of energy as a state-of-the-art lithium ion at a substantially lower cost. A team of scientists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory is using the precision of an electron beam to instantly adhere cathode coatings for lithium-ion batteries. This new development, as reported in the
A team of scientists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory is using the precision of an electron beam to instantly adhere cathode coatings for lithium-ion batteries. This new development, as reported in the