ECS Sensors Plus is pleased to highlight a recent contribution that showcases the power of material innovation in enhancing electrochemical sensing technologies. In their new article, “Application of a g-C₃N₄@nZVI/CNTs Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Uric Acid Detection in Spiked Urine Samples,” Aya A. Mouhamed, Ola G. Hussein, Maria Osama Mekhail, Tony Victor Zaki, Amr M. Mahmoud, and Jeffrey G. Bell present a promising approach for accurate, sensitive uric acid detection.
ECS Sensors Plus is pleased to highlight a recent contribution that showcases the power of material innovation in enhancing electrochemical sensing technologies. In their new article, “Application of a g-C₃N₄@nZVI/CNTs Modified Carbon Paste Electrode for Uric Acid Detection in Spiked Urine Samples,” Aya A. Mouhamed, Ola G. Hussein, Maria Osama Mekhail, Tony Victor Zaki, Amr M. Mahmoud, and Jeffrey G. Bell present a promising approach for accurate, sensitive uric acid detection.
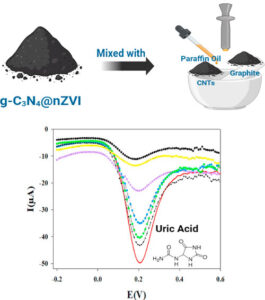
The research team developed a carbon paste electrode modified with a uniquely engineered g-C₃N₄@nZVI/CNT nanocomposite. By combining graphitic carbon nitride’s high surface area, nano zero-valent iron’s catalytic activity, and carbon nanotubes’ conductivity, the authors created a synergistic platform capable of boosting electron transfer and improving analytical performance.
Using differential pulse voltammetry, the sensor demonstrated a strong linear response (2.0–100.0 μM), a low detection limit (1.7 μM), and remarkable selectivity—even in the presence of common interferants. Its reliability, repeatability, and long-term stability underscore its potential for practical application.
Importantly, the modified electrode successfully detected uric acid in spiked urine samples, pointing to impactful uses in clinical diagnostics and environmental monitoring. This work highlights a scalable, cost-effective sensing strategy with strong translational potential.
Congratulations to the authors on this innovative contribution to the sensing community!