By: Blair Trewin, World Meteorological Organization
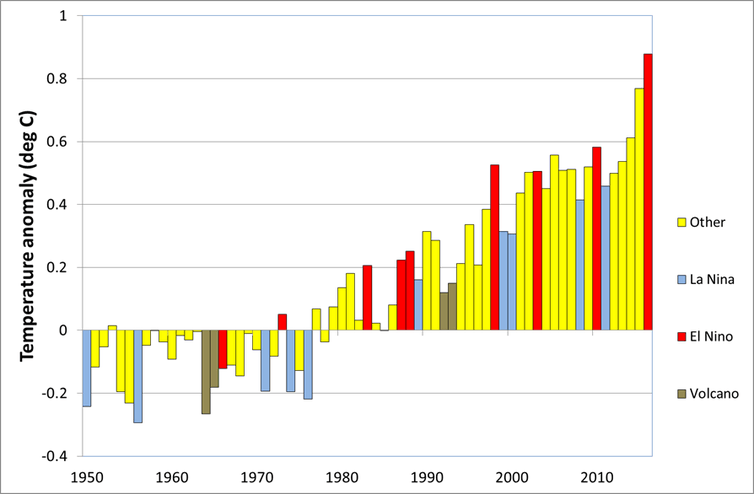
Global temperature anomalies (difference from 1961-90 average) for 1950 to 2016, showing strong El Niño and La Niña years, and years when climate was affected by volcanoes. (Click to enlarge.)
Image: World Meteorological Organization
2016 is set to be the world’s hottest year on record. According to the World Meteorological Organization’s preliminary statement on the global climate for 2016, global temperatures for January to September were 0.88°C above the long-term (1961-90) average, 0.11°C above the record set last year, and about 1.2°C above pre-industrial levels.
While the year is not yet over, the final weeks of 2016 would need to be the coldest of the 21st century for 2016’s final number to drop below last year’s.
Record-setting temperatures in 2016 came as no real surprise. Global temperatures continue to rise at a rate of 0.10-0.15°C per decade, and over the five years from 2011 to 2015 they averaged 0.59°C above the 1961-1990 average.
Giving temperatures a further boost this year was the very strong El Niño event of 2015−16. As we saw in 1998, global temperatures in years where the year starts with a strong El Niño are typically 0.1-0.2°C warmer than the years either side of them, and 2016 is following the same script.
Almost everywhere was warm
Warmth covered almost the entire world in 2016, but was most significant in high latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere. Some parts of the Russian Arctic have been a remarkable 6-7°C above average for the year, while Alaska is having its warmest year on record by more than a degree.
Almost the whole Northern Hemisphere north of the tropics has been at least 1°C above average. North America and Asia are both having their warmest year on record, with Africa, Europe and Oceania close to record levels. The only significant land areas which are having a cooler-than-normal year are northern and central Argentina, and parts of southern Western Australia.


