 Volatile fatty acids (VFAs) from biomass fermentation offer a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based chemicals, serving as building blocks for bioplastics, pharmaceuticals, and more. However, separating and purifying these acids from fermentation broths remains technically challenging.
Volatile fatty acids (VFAs) from biomass fermentation offer a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based chemicals, serving as building blocks for bioplastics, pharmaceuticals, and more. However, separating and purifying these acids from fermentation broths remains technically challenging.
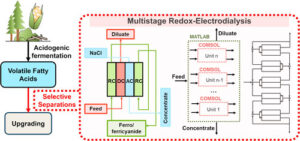
A new study in the Journal of The Electrochemical Society, selected as an Editors’ Choice article, addresses this bottleneck. Researchers Riccardo Candeago, Nidhish Lella, Wangsuk Oh, Ping Liu, and Xiao Su developed a physics-based model of redox-mediated electrodialysis (redox-ED) to optimize VFA separation strategies.
This work provides practical design tools for biorefinery operations, enabling better VFA recovery with existing membrane technologies. As the global VFA market approaches $2 billion by 2033, such innovations bridge the gap between laboratory research and industrial-scale sustainable production.
Read the full paper: “Editors’ Choice: Modeling of Multistage Redox-Mediated Electrodialysis for Volatile Fatty Acids Fractionation.”

