A new water-based air-conditioning system cools air to as low as 18 degrees Celsius (about 64 degrees Fahrenheit) without using energy-intensive compressors and environmentally harmful chemical refrigerants.
This technology could potentially replace the century-old air-cooling principle that is still used in modern-day air-conditioners. Suitable for both indoor and outdoor use, the new system is portable and can be customized for all types of weather conditions.
The team’s novel air-conditioning system is cost-effective to produce, and it is also more eco-friendly and sustainable.


 A team of researchers from the University of Toronto is looking to give wasted materials new value by developing a new catalyst that could help recycle carbon dioxide into plastic.
A team of researchers from the University of Toronto is looking to give wasted materials new value by developing a new catalyst that could help recycle carbon dioxide into plastic.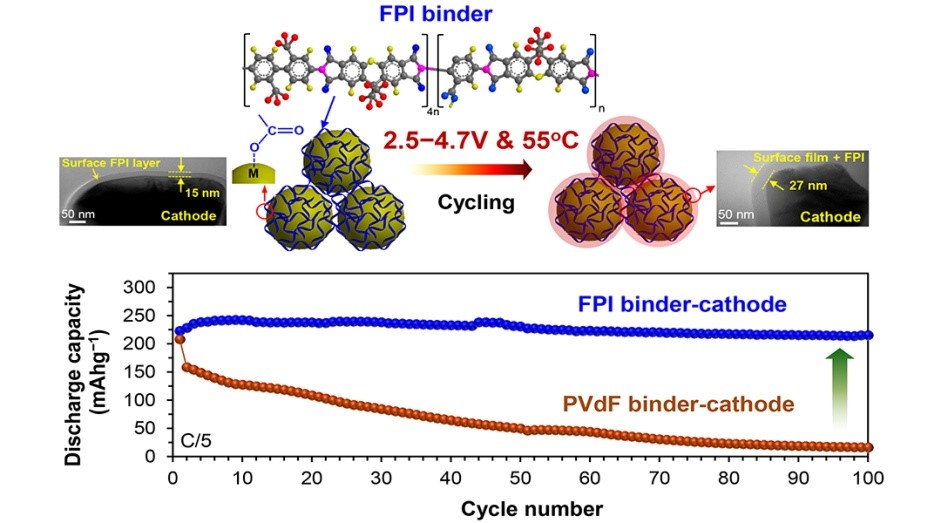
 One year ago, the Chinese government’s energy agency made a long-term commitment to the development of renewable energy sources, investing more than
One year ago, the Chinese government’s energy agency made a long-term commitment to the development of renewable energy sources, investing more than  Water-based rechargeable batteries could be one step closer to commercial viability, thanks to
Water-based rechargeable batteries could be one step closer to commercial viability, thanks to 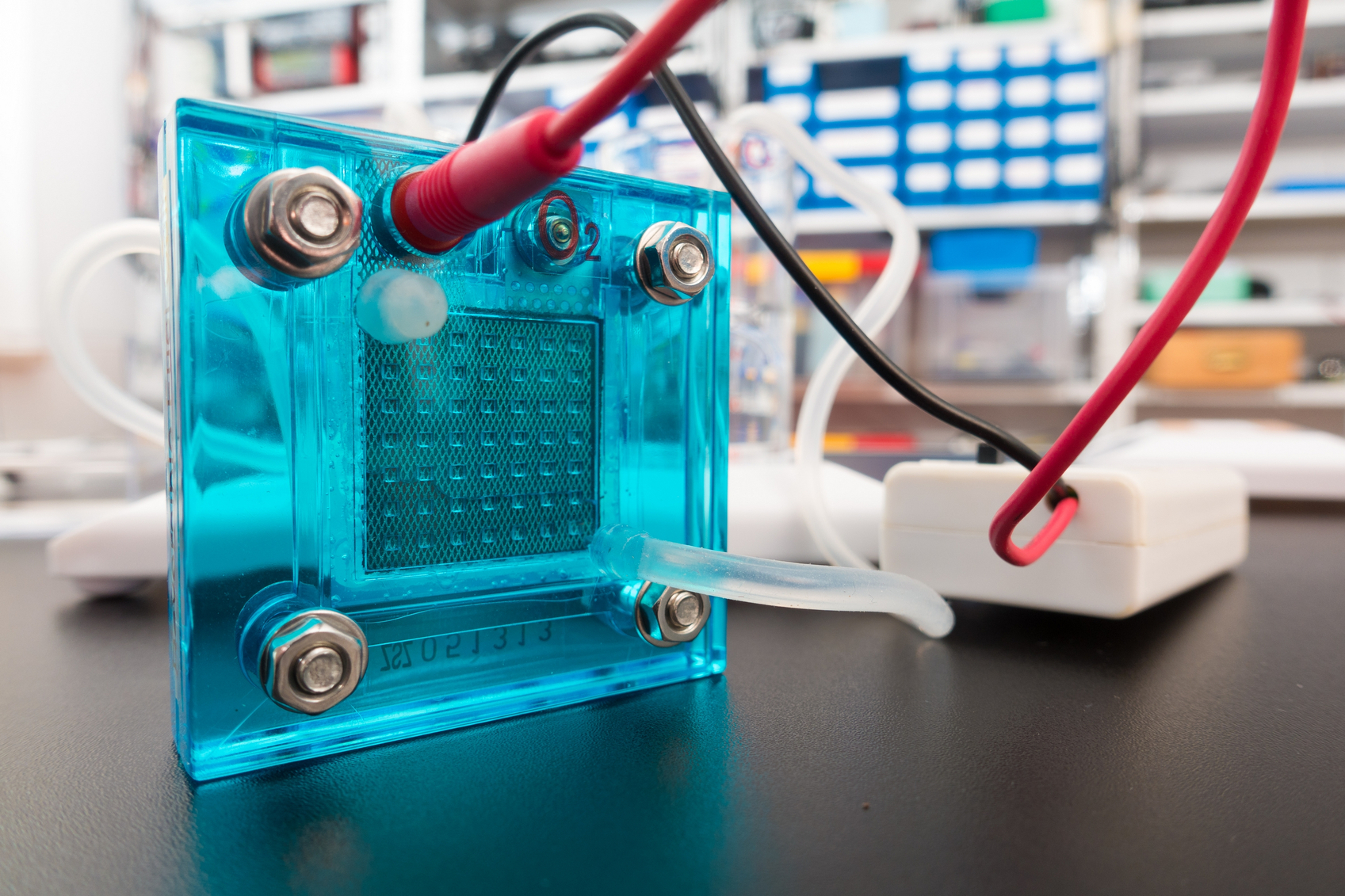 Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes or modified graphene nanoribbons could be effective, less costly replacements for expensive platinum in fuel cells, according to a new study.
Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes or modified graphene nanoribbons could be effective, less costly replacements for expensive platinum in fuel cells, according to a new study.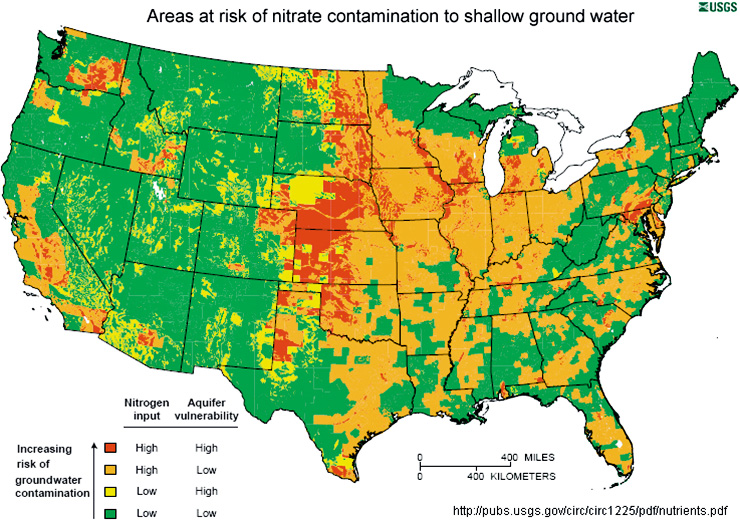
 ECS members
ECS members