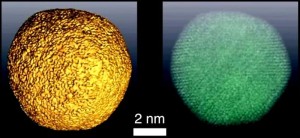
Engineers have developed a way to visualize the optical properties of objects that are thousands of times small than a grain of sand.
Source: YouTube/Stanford University
In order to develop high efficiency solar cells and LEDs, researchers need to see how light interacts with objects on the nanoscale. Unfortunately, light is tricky to visualize in relation to small-scale objects.
Engineers from Stanford University, in collaboration with FOM Institute AMOLF, have developed a next-gen optical method to produce high-resolution, 3D images of nanoscale objects. This allows researchers to visualize the optical properties of objects that are several thousandths the size of a grain of sand.
The teams achieved this by combining two technologies: cathodluminescence and tomography.