JSS Editors’ Choice article discusses AlGaN/GaN HEMTs
When it comes to putting technology in space, size and mass are prime considerations. High-power gallium nitride-based high electron mobility transistors (HEMTs) are appealing in this regard because they have the potential to replace bulkier, less efficient transistors, and are also more tolerant of the harsh radiation environment of space. Compared to similar aluminum gallium arsenide/gallium arsenide HEMTs, the gallium nitride-based HEMTs are ten times more tolerant of radiation-induced displacement damage.
Until recently, scientists could only guess why this phenomena occurred: Was the gallium nitride material system itself so inherently disordered that adding more defects had scant effect? Or did the strong binding of gallium and nitrogen atoms to their lattice sites render the atoms more difficult to displace?
The answer, according to scientists at the Naval Research Laboratory, is none of the above.
Examining radiation response
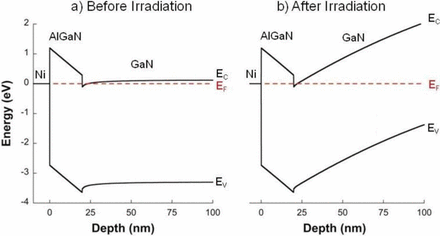
In a recent open access article published in the ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology entitled, “On the Radiation Tolerance of AlGaN/GaN HEMTs,” the team of researchers from NRL state that by studying the effect of proton irradiation on gallium nitride-based HEMTs with a wide range of initial threading dislocation defectiveness, they found that the pre-irradiation material quality had no effect on radiation response.
Additionally, the team discovered that the order-of-magnitude difference in radiation tolerance between gallium arsenide- and gallium nitride-based HEMTs is much too large to be explained by differences in binding energy. Instead, they noticed that radiation-induced disorder causes the carrier mobility to decrease and the scattering rate to increase as expected, but the carrier concentration remains significantly less affected than it should be.
(more…)


 While cyberwar may sound like the plot of the latest sci-fi blockbuster, the realities of the phenomena are much more palpable. Few understand that better than
While cyberwar may sound like the plot of the latest sci-fi blockbuster, the realities of the phenomena are much more palpable. Few understand that better than