By: Christopher Keane, Washington State University
 Emergency: You need more disposable diapers, right away. You hop into your car and trust your ride will be a safe one. Thanks to your phone’s GPS and the microchips that run it, you map out how to get to the store fast. Once there, the barcode on the package lets you accurately check out your purchase and run. Each step in this process owes a debt to the universities, researchers, students and the federal funding support that got these products and technologies rolling in the first place.
Emergency: You need more disposable diapers, right away. You hop into your car and trust your ride will be a safe one. Thanks to your phone’s GPS and the microchips that run it, you map out how to get to the store fast. Once there, the barcode on the package lets you accurately check out your purchase and run. Each step in this process owes a debt to the universities, researchers, students and the federal funding support that got these products and technologies rolling in the first place.
By some tallies, almost two-thirds of the technologies with the most far-reaching impact over the last 50 years stemmed from federally funded R&D at national laboratories and research universities.
The benefits from this investment have trickled down into countless aspects of our everyday lives. Even the internet that allows you to read this article online has its roots in federal dollars: The U.S. Department of Defense supported installation of the first node of a communications network called ARPANET at UCLA back in 1969.
As Congress debates the upcoming budget, its members might remember the economic impacts and improved quality of life that past congressional support of basic and applied research has created.

 Scientists have created a single catalyst that could simplify the process of splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen to produce clean energy.
Scientists have created a single catalyst that could simplify the process of splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen to produce clean energy. After months of hard work, ECS has launched an online membership wizard. Individuals who are interested in joining ECS as a student or as a member for one, two, three or five years are now able to complete their application online and have access to their ECS My Account.
After months of hard work, ECS has launched an online membership wizard. Individuals who are interested in joining ECS as a student or as a member for one, two, three or five years are now able to complete their application online and have access to their ECS My Account. The journal impact factors (JIFs) for 2016 have been released, and ECS is pleased to announce that the JIFs for the
The journal impact factors (JIFs) for 2016 have been released, and ECS is pleased to announce that the JIFs for the 
 Scientists have found that a common enzyme can speed up—by 500 times—the rate-limiting part of the chemical reaction that helps the Earth lock away, or sequester, carbon dioxide in the ocean.
Scientists have found that a common enzyme can speed up—by 500 times—the rate-limiting part of the chemical reaction that helps the Earth lock away, or sequester, carbon dioxide in the ocean. Brett Lucht is a professor of chemistry at the University of Rhode Island, where his research focuses on organic materials chemistry. Lucht’s research includes the development of novel electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries and other efforts to improve the performance of electrolytes for electric vehicles. Lucht has recently been named associate editor for the
Brett Lucht is a professor of chemistry at the University of Rhode Island, where his research focuses on organic materials chemistry. Lucht’s research includes the development of novel electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries and other efforts to improve the performance of electrolytes for electric vehicles. Lucht has recently been named associate editor for the  Scientists have found a way to make carbon both
Scientists have found a way to make carbon both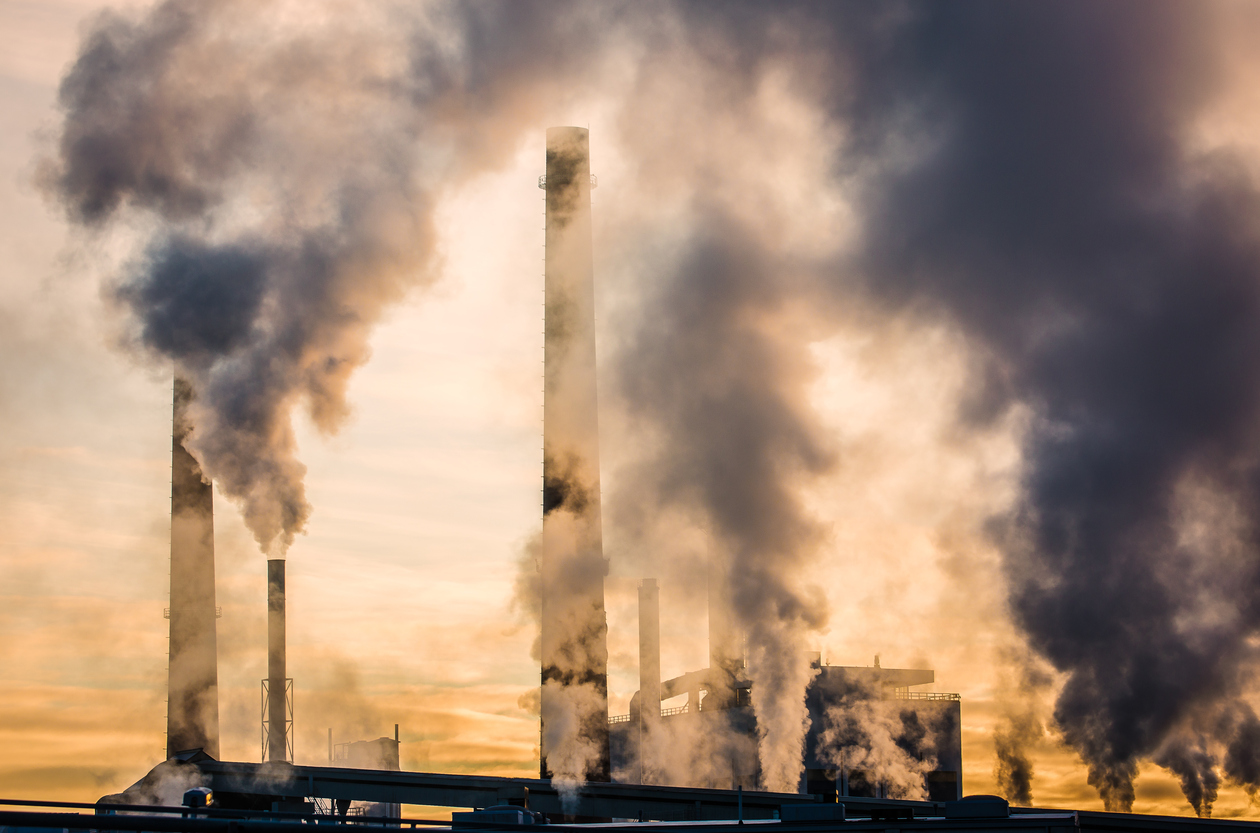  The global development of industry, technology, and the transportation sector has resulted in massive consumption of fossil fuels. As these fuels are burned, emissions are released—namely carbon dioxide. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, combustion of petroleum-based products resulted in
The global development of industry, technology, and the transportation sector has resulted in massive consumption of fossil fuels. As these fuels are burned, emissions are released—namely carbon dioxide. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, combustion of petroleum-based products resulted in