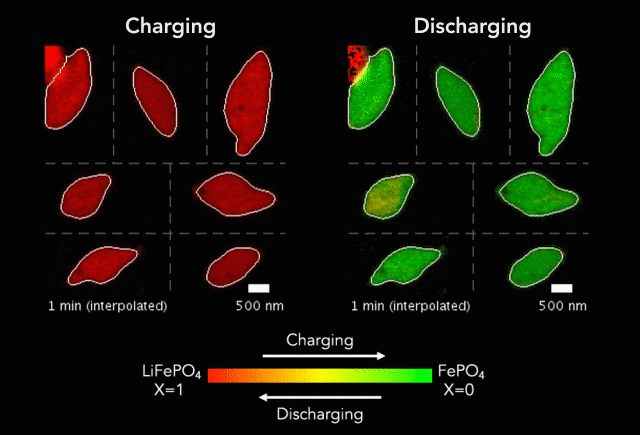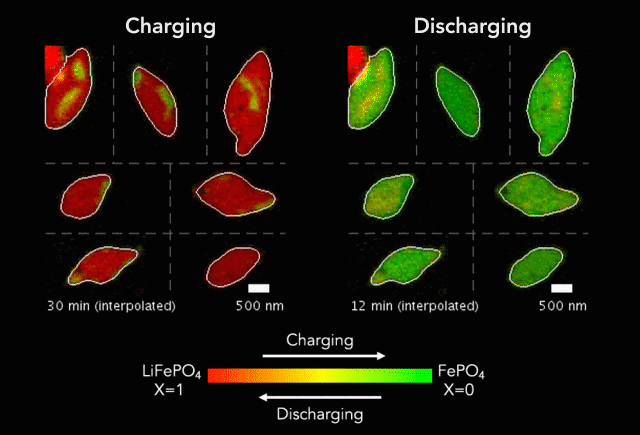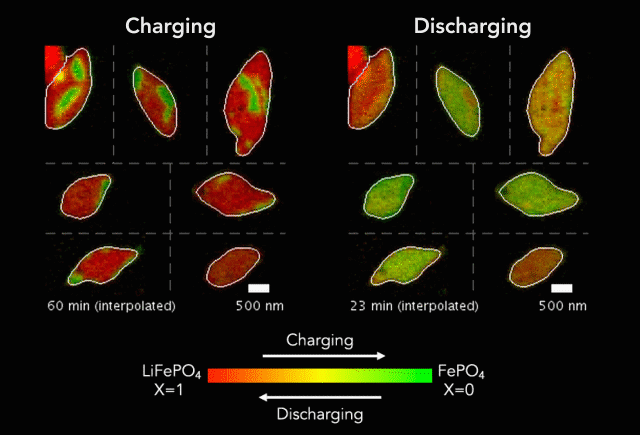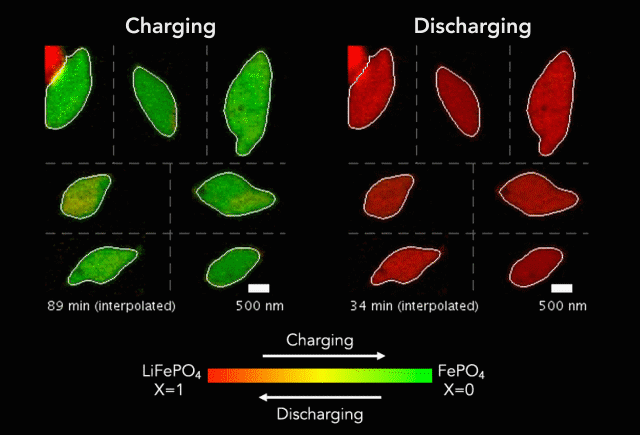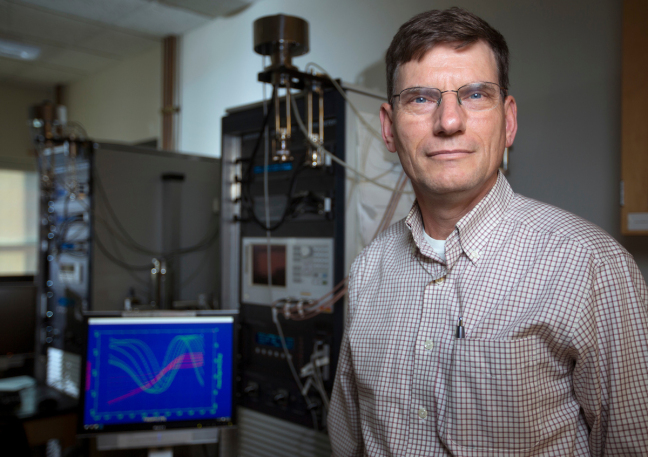
ECS member Steve Martin receives a $2.5M grant to pursue research in glassy solids.
Image: Christopher Gannon
The world relies on battery power. The smartphone market alone – which is powered by lithium-ion batteries – is expected to reach 1.5B units in 2016. ECS member Steve Martin believes he may be able to take those batteries to the next level through efforts in glassy solids.
Martin, a professor at Iowa State University and associate of the U.S. Department of Energy’s Ames Laboratory, has been in the field of battery research for over 30 years. Throughout that time, his main focus of research has shifted to measuring the basic properties of glassy solids and trying to understand how their ions move and the thermal and chemical stability.
Martin believes that using glass solids as the electrolytes in batteries would make them safer and more powerful. This is an effort to diverge from traditional liquid-electrolyte batteries, which have experienced issues with safety and energy capacity.
To push this research, Martin recently received a three-year, $2.5M grant from the DOE.
“This is my dream-come-true project,” Martin says. “This is what I’ve been working on for 36 years.”

 Lithium-air batteries are viewed by many as a potential next-generation technology in energy storage. With the highest theoretical energy density of all battery devices, Li-air could revolutionize everything from electric vehicles to large-scale grid storage. However, the relatively young technology has a few barriers to overcome before it can be applied. A new study published in the
Lithium-air batteries are viewed by many as a potential next-generation technology in energy storage. With the highest theoretical energy density of all battery devices, Li-air could revolutionize everything from electric vehicles to large-scale grid storage. However, the relatively young technology has a few barriers to overcome before it can be applied. A new study published in the